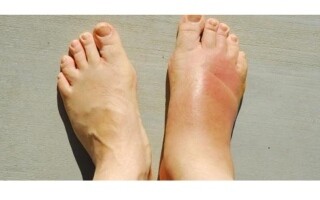
Doctor Roman Malkov, a specialist in gastrointestinal disorders and an expert in nutrition, explained that the term 'oteka' refers to the accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the organism, presenting itself in the form of edema and increased weight. According to him, the causes of edema are numerous and may be related to various disorders, such as heart failure, kidney diseases, allergic reactions, and a deficiency of protein in the blood.
To solve this problem, the immune system produces IgG-type antibodies, which leads to a delay in this type of allergy. "This is an immediate type of allergy, based on an increase in the production of IgE-type antibodies," added the specialist.
He also noted that hypersensitivity often manifests as a slow and concealed process, referred to as delayed allergy. Symptoms may not appear immediately after consuming a product, but only after several days or weeks after contact with allergens, which complicates the establishment of a causal relationship and may lead to errors in diagnosis and ineffective treatment.
For diagnosing hidden food hypersensitivity, it is essential to adhere to a comprehensive approach, as simple exclusion from the diet of certain products may turn out to be ineffective for identifying the cause. Food hypersensitivity is different from common allergies.
The doctor emphasized that allergies are an immune reaction that most often manifests quickly, with symptoms such as skin rashes, sneezing, watery eyes, shortness of breath, and in severe cases - anaphylactic shock. The primary role in the treatment of hypersensitivity is played by addressing the 'prone syndrome,' as it is the main complication, such as chronic inflammatory processes, edema, autoimmune disorders, and neurological disorders in the brain.
All these negative processes affect the inflammation of the intestinal lining, its destruction, and the appearance of lesions through which the contents of the intestine can enter the bloodstream. In this regard, the most accurate method is the analysis of IgG antibodies to food products.














